Business Analysis Planning and Monitoring
Chapter 3. Business Analysis Planning and Monitoring

Each Task in the BABOK Guide is presented in the following format:
- Purpose >
- Description >
- Inputs >
- Elements >
- Guidelines / Tools >
- Techniques >
- Stakeholders >
- Outputs >
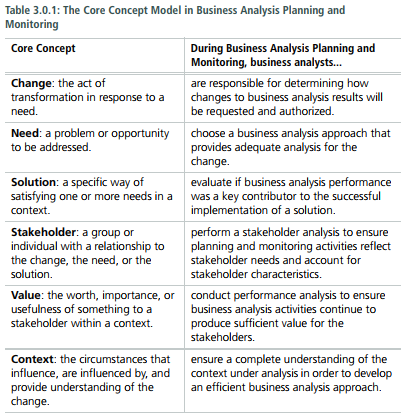
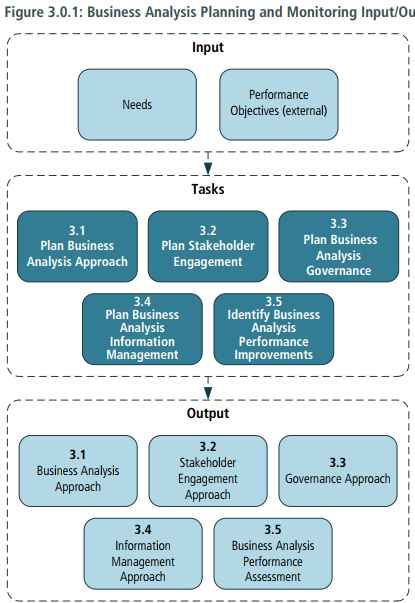
1. Business Analysis Approach
Decribes the planning of business analysis work from creationg or selection of a methodology to planning the individual activies, tasks, and deliverables.
- Purpose > define an appropriate method to conduct business analysis activities.
- Description > Align to the overall goals of the change > Coordinate the business analysis tasks with the activities and deliverables of the overall change >> Include tasks to manage any risk that could reduce the quality of business analysis deliverables or impede task efficiency, and > leverage approaches and select techniques and tools that have historically worked well.
- Inputs > Needs
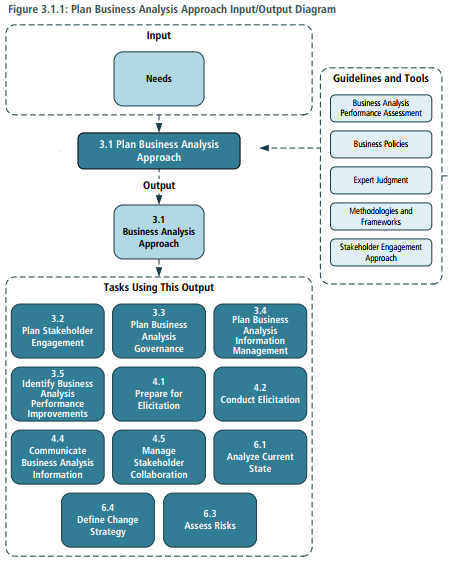
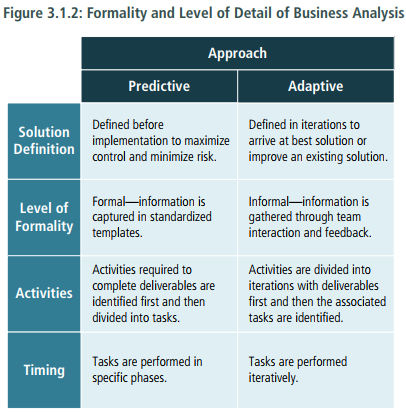
- Elements > Planning Approach > Formality and Level of Detail of Business Analysis Deliverables > Business Analysis Activities > Timing of Business Analysis Work > Complexity and Risk > Acceptance
- Guidelines / Tools > Business Analysis Performance Assessment > Business Policies > Expert Judgement > Methodologies and Frameworks > Stakeholder Engagement Approach
- Techniques > Brainstorming > Business Cases > Document Analysis > Estimation > Financial Analysis > Functional Decomposition > Interviews > Item Tracking > Lessons Learned > Process Modelling > Reviews > Risks Analysis and Management > Scope Modelling > Survey or Questionnarie > Workshops
- Stakeholders > Domain Subject Matter Expert > Project Manager > Regulator > Sponsor
- Outputs > Business Analysis Approach: identifies the business analysis approach and activities that will be performed across an initiative including who will perform the activities, the timing and sequencing of the work, the deliverables that will be produced and the business analysis techniques that may be utilized. The remaining outputs of the Business Analysis Planning and Monitoring knowlwgde area may be intergrated into an overall approach or be independent based upon methodology, organization, and perspective.
2. Plan Stakeholder Engagement
Descibes understanding which the stakeholders are relevant to the change, what business analyst need from them, what they need from business analysts, and the best way to collaborate.
- Purpose > The pủpose of Plan Stakeholder Engagement is to plan an approach for establishing and maintaining effective working relationship with the stakeholders.
- Description: involves conducting a thorough stakeholder analysis to identify all of the involved stakeholders and analyze their characteristics.
- Input > Needs > Business Analysis Approach
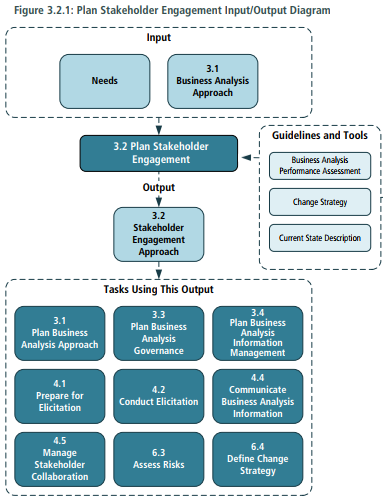
- Elements > Perform Stakeholder Analysis ( Roles - Attitudes - Decision Making Authority - Level of Power or Influence) > Define Stakeholder Collaboration > Stakeholder Communication Needs
- Guidelines / Tools > Business Analysis Performance Assessment > Change strategy > Current State Description
- Techniques > Brainstorming > Business Rules Analysis > Document Analysis > Interviews > Lessons Learned > Mind Mapping > Organization Modelling > Process Modelling > Risks Analysis and Management > Scope Modelling > Stakeholder List, Map, or Personas > Survey or Questionnarie > Workshops
- Stakeholders > Customers > Domain Subject Matter Expert > End User > Project Manager > Regulator > Sponsor > Supplier
- Outputs > Stakeholder Engagement Approach: Contain a list of the stakeholders, their characteristics which are analyzed, and a listing of roles and responsibilities for the change. It also identifies the collaboration and communication approaches the business analyst will utilize during the initiative.
3. Plan Business Analysis Governance
Defines the components of business analysis that are used to support the governance function of the organization. It helps ensure that decisons are made properly and consistently, and follows a process that ensures decision makers have the information they need. Examples of this include requirements management, business analysis risk management, and allocation of business analysis resource.
- Purpose > The purpose of Plan Business Analysis Governance is to define how decision are made about requirements and designs, including reviews, change control, approvals, and prioritization.
- Description: Business analysts ensure that a governance process is in place and clarify any ambiguities within it. A governance process indentifies the decision makers, process, and information required for decision to be made.
- Inputs > Business Analysis Approach > Stakeholder Engagement Approach
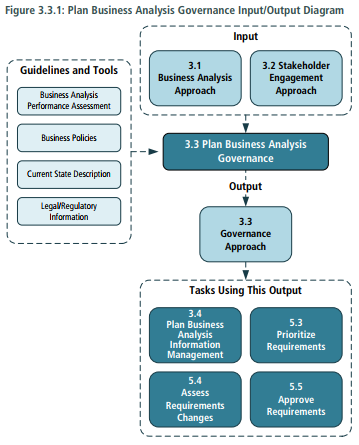
- Elements > Decision Making > Change Control Process > Plan Prioritization Approach > Plan for Approvals
- Guidelines / Tools > Business Analysis Performance Assessment > Business Policies > Current State Descripton > Legal / Regulatory Information
- Techniques > Brainstorming > Document Analysis > Interviews > Item Tracking > Lessons Learned > Organization Modelling > Process Modelling > Reviews > Survey or Questionnaire > Workshops
- Stakeholders > Domain Subject Matter Expert > Project Manager > Regulator > Sponsor
- Outputs: Governance Approach: identifies the stakeholder who will have the responsibility and authority to make decision about business analysis work including who will be responsible for setting priorities and who will approve changes to business analysis information. It also defines the process that will be utilized to manager requirement and design changes across the initiative.
4. Plan Business Analysis Information Management
Defines how information developed by business analyst (including requirements and designs) is captured, stored, and intergrated with other information for long-term use.
- Purpose > The purpose of Plan Business Analysis Information Management is to develop an approach for how business analysis information will be stored and accessd.
- Description: Business Analysis information is comprised of all the information business analyst elicit, create, compile, and disseminate in the course of performing business analysis. Models, scope statements, stakeholder concerns, elicitation results, requirements, designs, and solution options are just a few examples.
- Inputs > Business Analysis Approach > Governance Approach > Stakeholder Engagement Approach
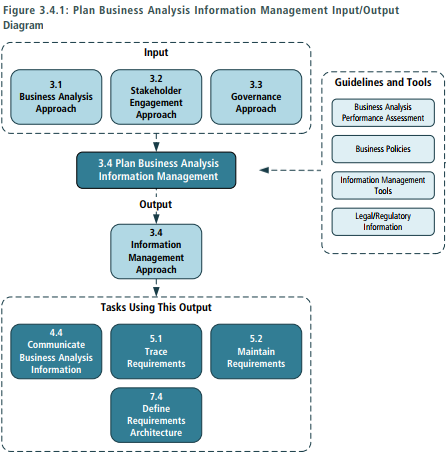
- Elements > Organization of Business Analysis Information > Level of Abstraction > Plan Traceability Approach > Plan for Requirements Reuse > Storage and Access > Requirements Attributes (Absolute reference - Author - Complexity - Ownership - Priority - Risks - Source - Stability - Status - Urgency)
- Guidelines / Tools > Business Analysis Performance Assessment > Business Policies > Information Management Tools > Legal / Regulatory Information
- Techniques > Brainstorming > Interviews > Item Tracking > Lessons Learned > Mind Mapping > Process Modelling > Survey or Questionnaire > Workshops
- Stakeholders > Domain Subject Matter Expert > Regulator > Sponsor
- Outputs > Information Management Approach : includes the defined approach for how business analysis information will be stored, accessed, and ultilized during the change and after the change is complete.
5. Identify Business Analysis Performance Improvements
Describes managing and monitoring how business analysis work is performed to ensure that commitment are met and continuous learning and improvement opportunities are realized.
- Purpose > The purpose of Identify Business Analysis Performance Improvement is to assess business analysis work and to plan to improve processes where required.
- Description: To monitor and improve performance, it is necessary to establish the performance measure,conduct the performance analysis, report on results of analysis, and indentify any necessary preventive, corrective, or developmental aactions. Performance analysis should occur throughout an initiative. Once potential peformance improvement are identified, they become guidelines for the next time a task is executed.
- Inputs > Business Analysis Approach > Performance Objecttives (external)
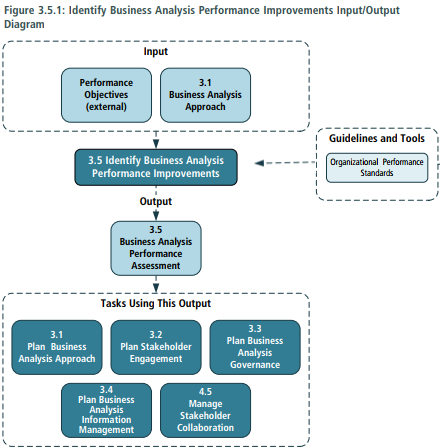
- Elements > Performance Analysis > Assessment Measure (Accuracy and Completeness - Knowlegde - Effictiveness - Organizational Support - Significance - Strategy - Timeliness) > Analyze Result > Recommend Action for Improvement (Preventive - Corrective - Improvement)
- Guidelines / Tools > Organization Performance Standards
- Techniques > Brainstorming > Interviews > Item Tracking > Lessons Learned > Metric and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) > Observation > Process Analysis > Process Modelling > Reviews > Risk Analysis and Management > Root Cause Analysis > Survey or Questionnaire > Workshops
- Stakeholders > Domain Subject Matter Expert > Project Manager > Sponsor
- Outputs > Business Analysis Performance Assessment: includes a comparision of planned versus actual performance, identifying the root cause of variances from the expected performance, proposed approaches to address issues, and other findings to help understand the performance of buisiness analysis processes.